
Data is a collection of raw or organized information which can be in the form of numbers, characters, images, video, audio, bytes, documents and several other forms. They can be facts, figures, measurements, graphs, raw unprocessed information etc.
TYPES OF DATA
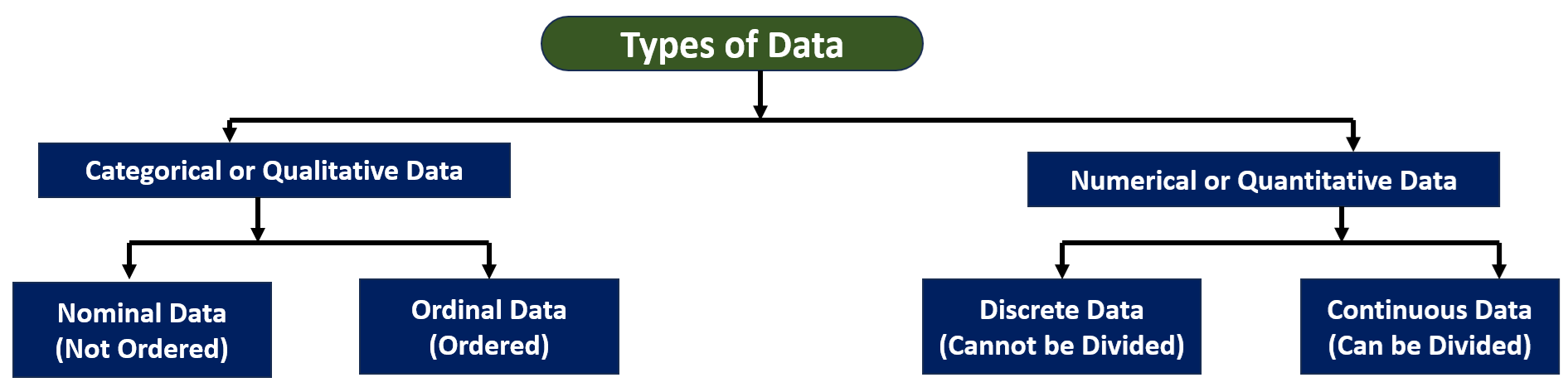
QUALITATIVE DATA

Qualitative data describes the data that fits into the categories. These are non-numerical in nature that describes qualities, characteristics, or concepts. Examples include a persons gender, town.
Sometimes categorical data can be numerical values (quantitative value), but these values do not have a mathematical sense.
They are further classified into Nominal Data and Ordinal Data.
Nominal Data
Nominal data is data that consists of categories or names that cannot be ordered or ranked. They are used to categorize the observations into groups, and these groups are not comparable.
E.g :
- Gender Groups : Male, Female, Undisclosed
- Ethnic Groups : White , Asian, Hispanic, White, Alaskan Native
- Hair Colour : Black , Brown, Blonde
- Nationality : Indian, American, French
- Transport : Bus, Train, Taxi
- Brands : Brand A, Brand B, Brand C
Ordinal Data
Ordinal data is data that consists of categories or names that can be ordered or ranked. Examples of ordinal data include education level. Ordinal data can help to compare one item with another by ranking or ordering
E.g :
- Grade Level : Grade I , Grade II, Grade III, Grade IV
- Education Level : SSC, HSC, Graduation, Masters, Phd
- Seniority Level : Junior, Mid, Senior
QUANTITATIVE DATA

Qualitative data describes the data represents the numerical value of the data.
E.g :
- Height , Weight , Room Temperature, Test Scores, Time
- Number of students in a class
- Number of Products in a Shop
They are classified into Discrete Data and Continuous Data.
Discrete Data
The discrete data is data that is distinct and separate. It is data that have a particular value rather than a range.They have countable values and are finite. Discrete contain values that fall under integers or whole numbers. Discrete Data is Countable. There are distinct or different values in discrete data.
E.g :
- Number of employees in a company
Continuous Data
They contain values that represent the data in a continuous range. The variable in the data set can have any value between the range of the data set. Continuous Data is Measurable. Every value within a range is included in continuous data. The data that lies between the highest and the lowest value are called the continuous data. The range of the continuous data is the difference between the highest and the lowest data.
E.g :
- Temperature Range
- Salary Range
- Time
- Length
- Mass
- Capacity